Figure 5.
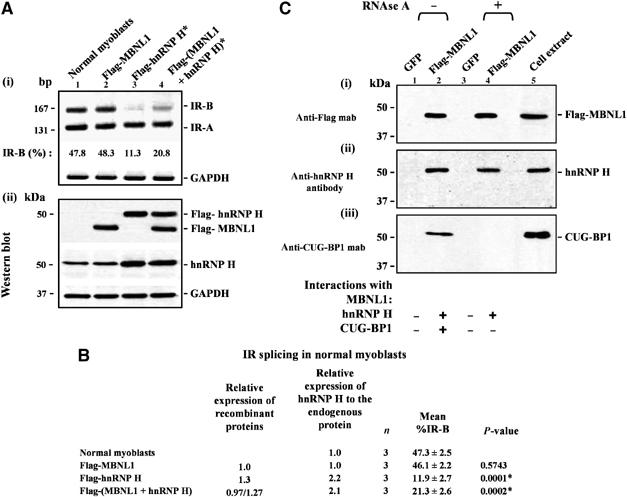
Overexpression of MBNL1 partially rescues the IR splicing defect resulting from elevated levels of hnRNP H in normal myoblasts and MBNL1 interacts with hnRNP H in an RNA-independent manner in vivo. (A) Normal myoblasts were transfected with Flag-MBNL1, Flag-hnRNP H or Flag-MBNL1 and Flag-hnRNP H in combination. Total RNA was isolated 48 h post-transfection and subjected to RT–PCR analyses using IR primers. GAPDH RNA was amplified in parallel as an internal control. Levels of IR-B obtained in the experiment shown in (i) are indicated. (ii) Total protein (10 μg) was analyzed by Western blots to measure the levels of expressed MBNL1 and hnRNP H using anti-Flag and anti-hnRNP H antibodies, respectively. The blots were re-probed for GAPDH as a loading control. (B) The results of three independent experiments are tabulated. The asterisk (*) represents significant differences from the control (Student's two-tailed t-test; P<0.05). (C) Normal myoblasts were transduced with recombinant adenoviruses expressing Flag-MBNL1 or GFP. At 48 h postinfection, total cell extracts were prepared and incubated with anti-Flag beads to immunoprecipitate proteins under non-RNAse and RNAse treatment conditions. The eluted proteins from each immunoprecipitation were analyzed by Western blot staining with anti-Flag mab (i), anti-hnRNP H polyclonal antibodies (ii), and anti-CUG-BP1 mab (iii). Staining with anti-Flag mab demonstrates the precipitation of Flag-MBNL1 (i). (ii) Staining with anti-hnRNP H polyclonal antibodies demonstrates that endogenous hnRNP H co-immunoprecipitates with Flag-MBNL1 both under non-RNAse and RNAse treatment conditions. (iii) CUG-BP1 mab staining demonstrates that CUG-BP1 co-immunoprecipitates with Flag-MBNL1 only under non-RNAse treatment conditions.
