Figure 2.
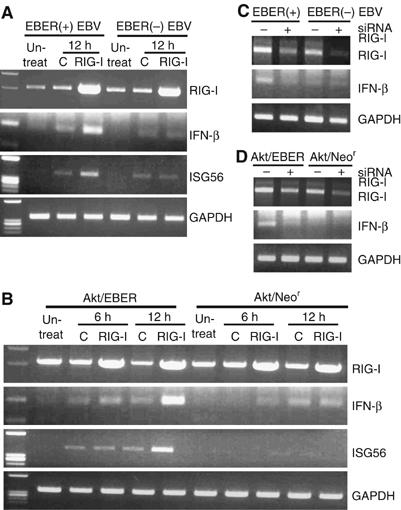
RIG-I induces type I IFN in EBER-expressing cells. BL-derived, EBER-positive and EBER-negative Akata cells (5 × 106 each) were transfected with 30 μg of GFP-tagged RIG-I plasmid or GFP plasmid, and expression of IFN-β and ISG56 was examined at the designated time by RT–PCR. (A) Expression of IFN-β and ISG56 in Akata cells infected with EBER-knockout EBV (EBER(−) EBV) or EBER-reintroduced EBV (EBER(+) EBV). After 12 h of transfection of the RIG-I plasmid or control plasmid, cells were subjected to RT–PCR analysis. (B) Expression of IFN-β and ISG56 in Akata cells stably transfected with EBER plasmid (Akt/EBER) or in those with control plasmid carrying the neomycin resistance gene (Akt/Neor). After 6 and 12 h of transfection of the RIG-I plasmid or GFP plasmid, cells were subjected to RT–PCR analysis. (C) EBER-positive EBV-infected and EBER-negative EBV-infected Akata cells were transfected with 100 nM of RIG-I siRNA or control siRNA. After 24 h, expression of RIG-I and IFN-β was checked by RT–PCR. (D) EBER-expressing Akata cells and control cells were also transfected with 100 nM of RIG-I siRNA/control siRNA and the expression of RIG-I and IFN-β was examined at 24 h post-transfection.
