Figure 1.
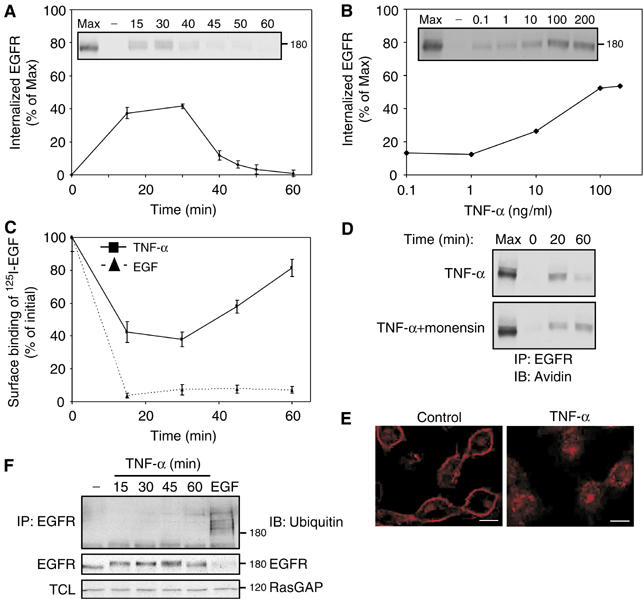
Cytotoxic cytokines induce transient internalization of EGFR with no associated ubiquitinylation or degradation. (A) Following surface biotinylation, HeLa cells were treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) for the indicated time intervals. Subsequently, surface-accessible biotin was cleaved, cells were lysed, and EGFR immunoprecipitated and detected in blots using streptavidin-HRP (inset). Quantification of signals corresponding to internalized receptor molecules is shown, relative to maximal surface labeling (Max), measured in the absence of a biotin cleavage step. Bars represent standard deviation values of three identical experiments. (B) Cells were treated for 30 min as in (A), except that increasing concentrations of TNF-α were used. (C) Downregulation of EGFR was tested in HeLa cells, which were treated with TNF-α or with EGF (100 ng/ml, each) for the indicated time intervals. Bars represent standard deviations of triplicate determinations. (D) HeLa cells were left untreated, or pretreated with monensin (100 μM; 15 min). Cells were then incubated with a cleavable biotin, followed by treatment with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of monensin, prior to analysis. (E) HeLa cells were left untreated or treated for 30 min with TNF-α (100 ng/ml). Cells were then fixed, permeabilized with methanol and stained with an anti-EGFR antibody, followed by an anti-mouse Cy3 antibody. Confocal microscopy images were taken from a middle section of the cell. Bars, 10 μm. (F) HeLa cells were left untreated, treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) for the indicated time intervals, or treated with EGF (10 ng/ml; 5 min). EGFR immunoprecipitates (IP) or total cell lysates (TCL) were immunoblotted (IB) using the indicated antibodies.
