Figure 3.
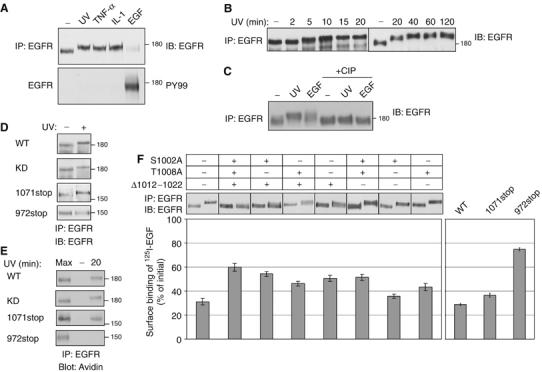
Stress induces phosphorylation at the carboxyl-tail of EGFR. (A) HeLa cells were UV irradiated (20 min), or treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml; 30 min), IL-1 (10 ng/ml; 30 min) or EGF (10 ng/ml; 5 min). EGFR immunoprecipitates were probed with anti-EGFR and anti-phosphotyrosine (PY99) antibodies. (B) HeLa cells were UV irradiated, allowed to recover for the indicated time intervals, and immunoprecipitated EGFR analyzed. (C) HeLa cells were left untreated, UV irradiated (followed by 20 min recovery), or treated with EGF (10 ng/ml; 5 min). Following immunoprecipitation, EGFR was incubated for 30 min at 37°C without or with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP; 20 U). (D) HeLa cells stably expressing EGFR-specific siRNA, were transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated EGFR mutants bearing silent mutations at the siRNA target sequence. After 48 h later, cells were UV irradiated, or left untreated, and let to recover at 37°C for 20 min prior to analysis. (E) Surface biotinylated cells expressing EGFR-specific siRNA, along with the respective EGFR mutant, were left untreated (lanes labeled −), or UV irradiated, and allowed to recover for 20 min at 37°C. Internalized EGFR was detected with streptavidin-HRP. For control, cell extracts were analyzed immediately following UV irradiation (lanes labeled Max). (F) HeLa cells expressing EGFR-specific siRNA were transfected with plasmids encoding the indicated EGFR mutants were untreated or treated with UV irradiation and extracts were analyzed as in (D). Following irradiation, sister cultures were incubated for 90 min on ice with a radiolabeled EGF. EGF binding results were calculated after subtraction of nonspecific binding. Bars represent standard deviation values of quadruplets.
