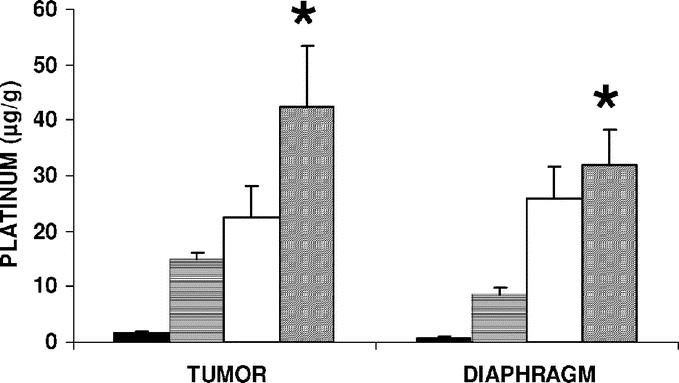
FIGURE 1. Platinum concentration in peritoneal tumors and diaphragm after IV, IP, or IAP cisplatin treatment. Rats with 21-day-old carcinomatosis (5 per group) were treated with cisplatin by intravenous (IV) or conventional intraperitoneal (IP) injection, or by a 1-hour intraperitoneal infusion with a sustained 22 mm Hg intra-abdominal pressure (IAP). The cisplatin dose was 1 mg/rat (3 mg/kg) for the IV administration (dark bars) and 7.5 mg/rat (22.5 mg/kg; 50 mg/L in 150 mL of isotonic saline) for the IAP treatment (diagonal bars). For the conventional IP treatments, cisplatin was given either to obtain the same concentration (50 mg/L in 20 mL; 1 mg/rat; 3 mg/kg; horizontal bars) or the same total dose (7.5 mg/rat; 22.5 mg/kg; 375 mg/L in 20 mL; clear bars) as for the IAP treatment. Each point is the average of 5 determinations and presented as a mean value; bars = SD. *Statistically significant difference between the IAP group and both the conventionally treated IP groups, either at the same concentration or at the same total dose of cisplatin (P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test).
