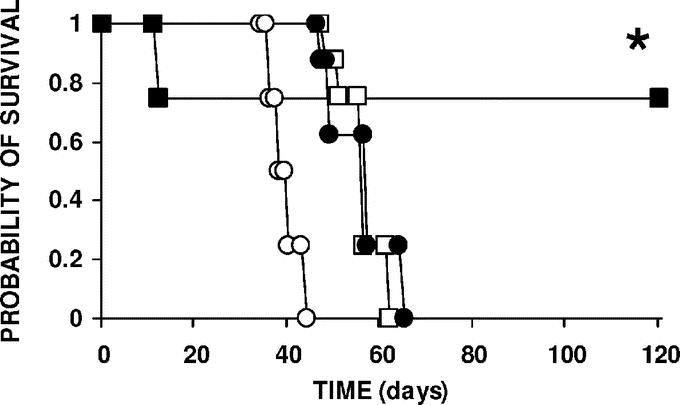
FIGURE 4. Animal survival according to treatment. Rats with 14-day-old carcinomatosis (8 per group) were treated with cisplatin by the intravenous (•) (IV) or the intraperitoneal (IP) route with (IAP, ▪) or without increased intra-abdominal pressure (IP conventional; □). Control animals (○) were left untreated. Cisplatin was given at the maximum tolerated dose for IV administration (1 mg/rat; 3 mg/kg). For conventional IP chemotherapy, rats received 20 mL of the 50 mg/L cisplatin solution (1 mg/rat; 3 mg/kg) as a bolus into the peritoneal cavity. For IP chemotherapy with IAP, cisplatin was administered in 150 mL of isotonic saline solution, 50 mg/L (7.5 mg/rat; 22.5 mg/kg), and continuously infused for 1 hour to maintain a constant 22 mm Hg intra-abdominal pressure. In both IP-treated groups, the peritoneal cavity was emptied and washed with drug-free saline 1 hour after starting the treatment. Animals were kept until spontaneous death or sacrifice at 120 days. *Significantly prolonged survival in the group treated with IP cisplatin with IAP compared with the conventionally treated IP group (log-rank test, P = 0.0157).
