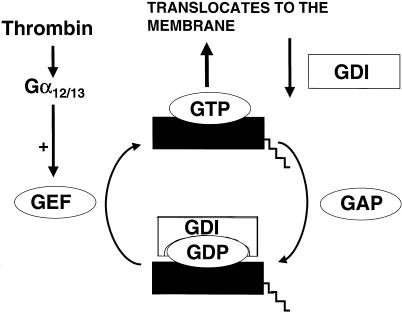
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of the activation of the RhoA. The GTP binding form of RhoA is translocated to the membrane where it is active. Guanine exchange factors (GEFs) activate RhoA, while GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) bring RhoA back to its inactive form. The guanine dissociation factors (GDIs) dissociate active RhoA from the membrane, facilitate its inactivation, and inhibit its activation by binding to the carboxyl-terminal part of RhoA.