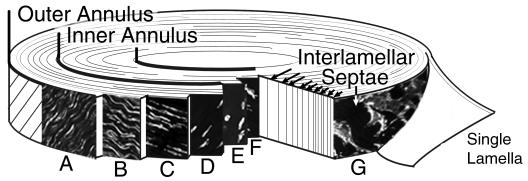
Fig. 2.
Division of the outer and inner annulus zones by identification of cell morphology. The outer annulus is characterized by cells with a fusiform cell body and a gradual transition in process architecture, while the inner annulus consists of cells with a spherical morphology. A–D. Outer Annulus: (A) A dense network of cells with cord-like processes in the longitudinal direction. (B,C) Cells with lateral and reduced length longitudinal processes. (D)Fusiform cells without processes. E,F. Inner Annulus: Cells with extensive, sinuous processes interspersed among spherical cells with at most two short processes. G. Interlamellar septae: a population of disc-shaped cells with a unique process architecture identified between the lamellar layers of the outer annulus.