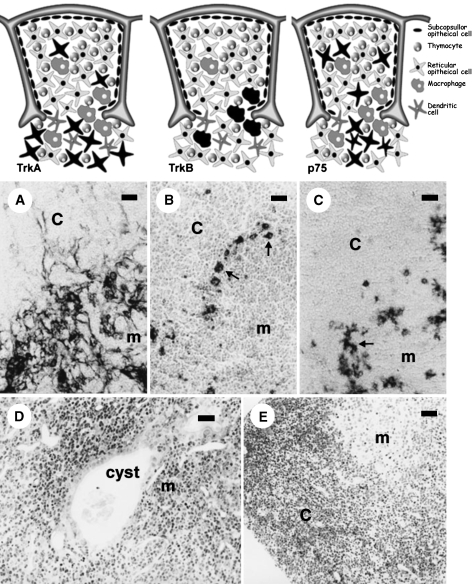
Fig. 2.
The upper pictures illustrate the localization of TrkA-(left), TrkB-(middle) and p75NTR (right)-positive cells in the rodent thymus; receptor-expressing cells are represented in black. Below are shown the corresponding TrkA (A), TrkB (B) and p75NTR (C) immunostained sections. The cells expressing TrkA are subcapsular and medullar thymic epithelial cells (mouse); those showing TrkB immunoreactivity, concentrated at the cortico-medullary border (arrows), are macrophages (rat), and p75NTR immunoreactivity is confined to a subpopulation of medullar thymic epithelial cells (arrows, rat). The lower images correspond to morphological aspects of functionally trkA- and trkB-deficient mice. The trkA-kinase –/– mouse thymus (D) is characterized by disorganization of the thymic architecture and the presence of medullar endodermic cysts containing amorphous material and cell debris, whereas the trkB-kinase –/– mouse (E) shows images of apoptotic lymphocyte death, especially in the cortex. c, cortical; m, medullar. Scale bar = 5 µm.