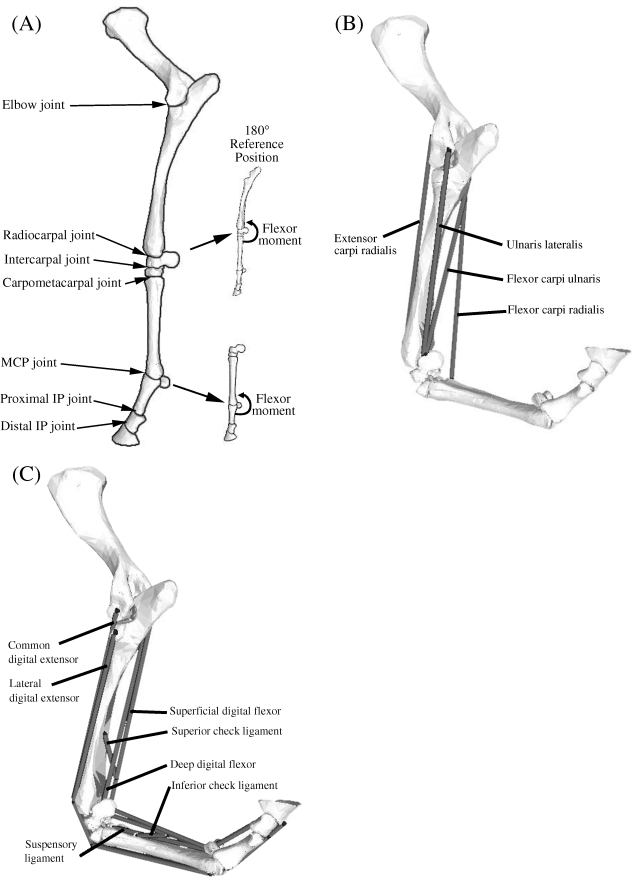
Fig. 1.
(A) Seven joints were included in the model of the equine forelimb: elbow, radiocarpal, intercarpal, carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal (MCP), proximal interphalangeal (IP) and distal interphalangeal (IP) joint. The reference position for the carpal and MCP joints was taken to be 180° with the limb extended, and flexor moments were defined on the caudal aspect of each joint as shown. (B) Computer-screen shot showing some of the muscles crossing the carpus in the model of the distal forelimb. Shown are the paths, origins, via points and insertions of the extensor carpi radialis, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris and ulnaris lateralis. The abductor pollicis longus muscle is not shown as it is located behind the radius and ulnar bones. (C) Computer-screen shot showing the muscles and ligamentous structures crossing the MCP joint in the model. Shown are the paths, origins, via points and insertions of the superficial digital flexor, deep digital flexor, the suspensory ligaments, and the superior and inferior check ligaments. The common and lateral digital extensor muscles are also shown, the former obscured partially by its lateral counterpart. Note that the superior check ligament and the inferior check ligament are tendinous extensions of the deep digital flexor (DDF) and the superficial digital flexor (SDF), respectively.