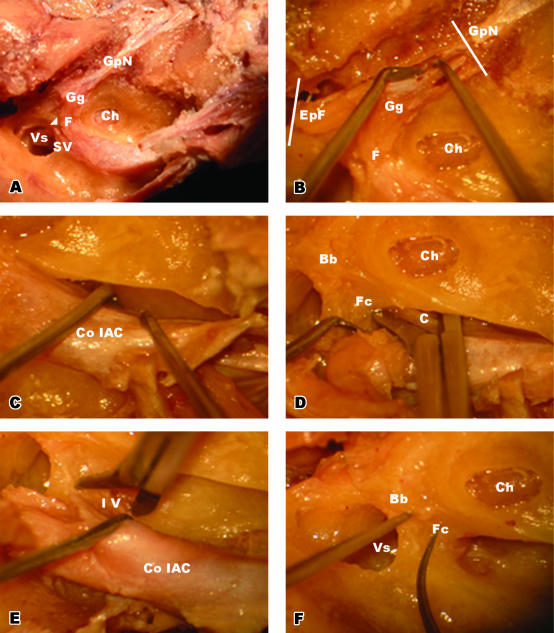
Fig. 1.
(A)Postero-superior view of the IAC. Bill's bar (arrowhead) is marked between the facial and superior vestibular nerves. (B) Dissection of ganglionic end of the facial nerve. The greater petrosal nerve and epitympanic end of the facial nerve were cut at the planes indicated with the white bars and released towards the IAC. (C) Removal of the IAC content within the dura from the bony structures. (D) Releasing process of the cochlear nerve at the inner end of the IAC. At the level of the cochlea, the cochlear nerve was cut after retracting the facial nerve posteriorly. (E) Releasing process of the inferior vestibular nerve at the inner end of the IAC. At the level of the vestibulum, the inferior vestibular nerve was cut after further retraction of the facial nerve. (F) Bony landmarks (Bill's bar and falciform crest) were identified after removing the content of the IAC. Abbreviations: Bb, Bill's bar; C, cochlear nerve; Ch, cochlea; Co IAC, content of internal auditory canal; EpF, epitympanic end of the facial nerve; F, facial nerve; Fc, falciform crest; Gg, geniculate ganglion; GpN, greater petrosal nerve; IV, inferior vestibular nerve; SV, superior vestibular nerve; Vs, vestibulum.