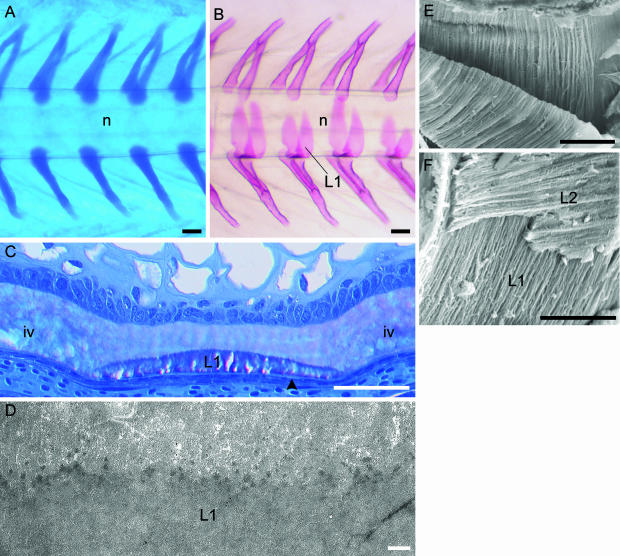
Fig. 2.
Development of the vertebral column of salmon. Formation of the neural and haemal arch cartilages and chordacentra (layer 1 of the vertebral body). (A,B) Micrographs of the caudal region of whole specimens. (A) Alcian blue staining showing the paired neural and haemal arch cartilages, which are situated directly on the external elastic membrane of the notochord. The notochord (n) is indicated. Developmental stage: 400 d°. (B) Alizarin red staining displaying layer 1 (L1) that develops as chordacentra within the notochordal sheath, from the ventral midline. Eventually this layer forms complete mineralized rings that increase in width in both cranial and caudal directions. Thus during early developmental stages, the vertebrae are cylindrical and acquire an amphicoelous shape as the layers external to the chordacentra are formed. The notochord (n) is indicated. Stage: 680 d°. (C) Methacrylate-embedded tissue stained with toluidine blue. Longitudinal section of the ventral part of the notochord. At this stage (700 d°) the notochordal sheath is divided into vertebral and intervertebral (iv) regions. In the vertebral regions layer 1 (L1) (chordacentra) are located in the external half of the notochordal sheath, covered by the external elastic membrane (arrowhead). (D) TEM micrograph of a longitudinal section of the notochordal sheath with a chordacentrum (L1). Stage: 700 d°. At the border between the chordacentrum and the remaining inner non-mineralized part of the notochordal sheath, multifocally distributed electron-dense areas are found. These may constitute initial centra of mineralization. (E) SEM micrograph of a chordacentrum that has been cut longitudinally and torn in two in order to expose the internal matrix structure. The collagen fibres are arranged in parallel cords (d about 1 µm), which run circumferentially in relation to the notochord. (F) Relation between layer 1 (L1) and layer 2 (L2), which both have ordered collagen matrixes that are orientated perpendicular to each other. Scale bars (A,B) 100 µm; (C) 50 µm; (D) 1 µm; (E) 50 µm; (F) 25 µm.