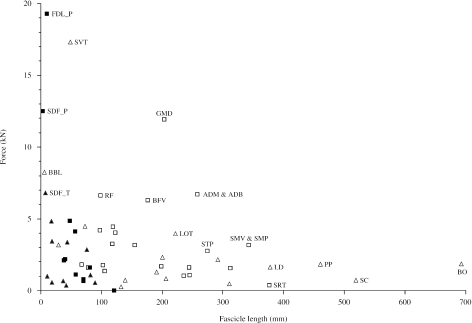
Fig. 5.
A comparison of maximum force and mean fascicle length for pelvic and thoracic limb muscles. Data are of proximal (solid squares) and distal (open squares) pelvic limb and proximal (solid triangles) and distal (open triangles) thoracic limb muscles. Thoracic limb extrinsic muscle data are from Payne et al. (2005); supraspinatus, biceps brachii and triceps brachii are from Watson (2004) and all other intrinsic muscle data are from Brown et al. (2003a). Thoracic limb muscle abbreviations: SVT (serratus ventralis thoracis); BBL (lateral head of biceps brachii); SDF_T (thoracic limb flexor digitorum superficialis); SC (subclavius); LD (latissimus dorsi); BO (brachiocephalicus and omotransversarius); LOT (long head of triceps brachii); PP (pectoralis profundus). Force (Fmax) was estimated from muscle PCSA and maximum isometric stress of skeletal muscle (0.3 MPa, Woledge et al. 1985; Zajac, 1989; Medler, 2002). Only those muscles with high force and/or long fascicle lengths are labelled.