Fig. 4.
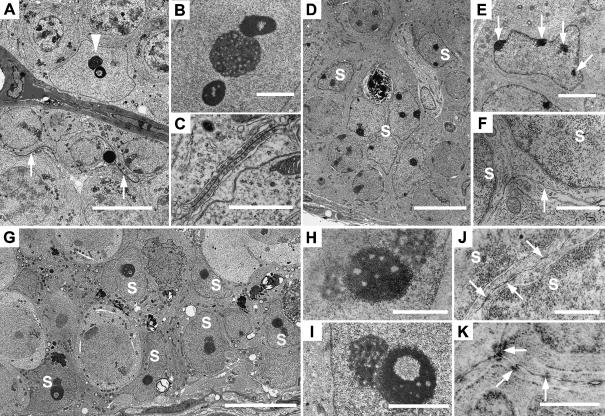
Electron micrographs of adult wild-type (A–C), 10-day wild-type (D–F) and adult hpg testes (G–K). (A) Typical normal adult Sertoli cell with nucleolus and annular chromatin (arrowhead) and curved inter-Sertoli cell junctions (arrows). (B) Sertoli cell tripartite nucleolar complex showing central nucleolus and flanking chromatin. (C) Inter-Sertoli cell junctional complex between apposing Sertoli cells. (D) Ten-day testis with compacted immature Sertoli cell nuclei (S). (E) Immature Sertoli cell nucleus with patches of heterochromatin associated with nuclear membrane (arrows). (F) Unspecialized plasma membranes (arrow) between adjacent Sertoli cell nuclei (S). (G) hpg testis showing basal and more central Sertoli cell nuclei (S). (H) Sertoli cell tripartite nucleolar complex with central chromatin and peripheral nucleoli. (I) hpg Sertoli cell nucleolar complex showing granular nucleolus and annular chromatin. (J) Plasma membranes between hpg Sertoli cell nuclei (S) showing segments of close apposition of membrane. (K) Plasma membranes between adjacent hpg Sertoli cells showing individual cytoplasmic densities. Scale bars in A,D,G = 10 µm; E = 3 µm; B,I = 2 µm; C,F,H = 1 µm; J,K = 0.5 µm.