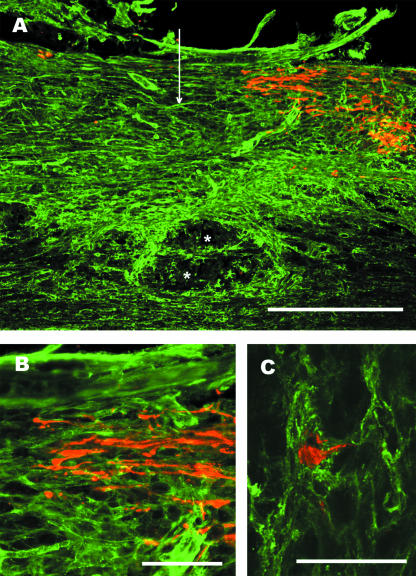
Fig. 4.
Lesioned mechanosensory axons end in an NG2-rich region of the glial scar. Adult rats were subjected to dorsal-over hemisections of the thoracic spinal cord and ascending mechanosensory axons retrogradely labelled by the injection of cholera toxin B subunit into the sciatic nerve 5 days post-lesion. Two days later the animals were killed and the tissue prepared for anti-NG2 (green) and anti-cholera toxin (red) immunofluorescence labelling. (A) NG2 immunoreactivity is increased surrounding and within the lesion centre. The vertical arrow marks the lesion centre and the asterisks indicate a cyst forming near the central canal. Scale bar = 500 µm. (B) Higher power view showing that the retrogradely labelled axons end with dystrophic end bulbs in a area with dense anti-NG2 stain. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) A dystrophic end bulb is encased in NG2-positive processes. This is a z-stack made from 18 1-µm-thick scans taken with a Ziess 510 confocal microscope. Scale bar = 50 µm.