Figure 3.
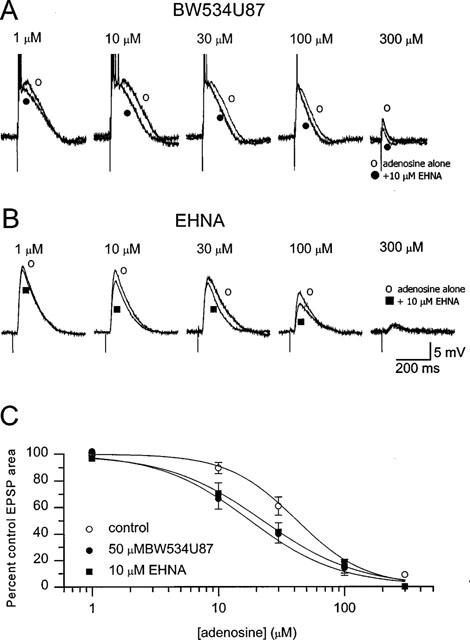
BW534U87 and EHNA enhanced the inhibitory effects of exogenous adenosine on evoked synaptic potentials. (A) Inhibition of the EPSP area in a CA1 pryramidal neurone by increasing concentration of exogenously applied adenosine (1–300 μM alone or in the presence of 50 μM BW534U87. (B) Inhibition of the EPSP by adenosine alone or in the presence of 10 μM EHNA. (C) Concentration-response curves for adenosine in the absence of drug (pooled data from nine cells) and in presence of BW534U87 (n= 5 cells) or 10 μM EHNA (n=4 cells). The smooth curves were obtained by fitting the data to an independent-binding-site receptor model. The IC50 for inhibition of the EPSP area by adenosine was estimated at 41.0 μM [29.8–53.9 μM) and a Hill coefficient was 1.8±0.1. In the presence of BW534U87 (50 μM), the IC50 for adenosine was 15.9 μM [7.3–25.8 μM] and the Hill coefficient was 1.5±0.1. In the presence of EHNA (10 μM) the IC50 for adenosine was 18.9 μM [11.7–30.6 μM] and the Hill coefficient was 1.5±0.2.
