Figure 5.
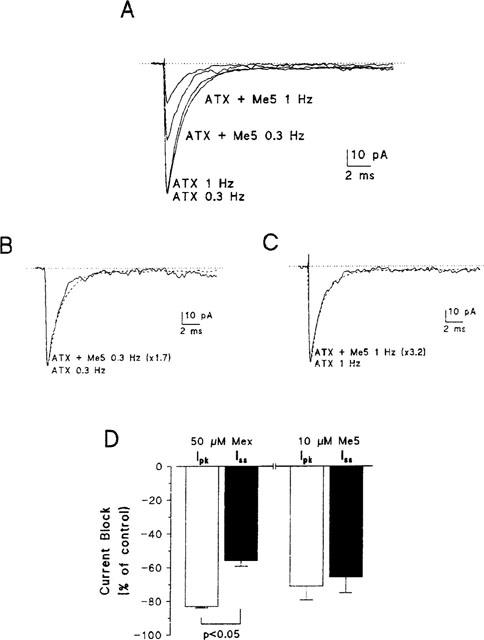
Effect of Me5 on macroscopic-current-like sodium currents recorded in the presence of ATX in a cell-attached patch of rat skeletal muscle fibre and comparison to the effects of mexiletine. (A) Ensemble average sodium currents constructed from 30 consecutive traces elicited by depolarizing the patch membrane from a holding potential of −100 mV to −20 mV, at stimulation frequencies of 0.3 Hz or 1 Hz, in the presence of 5 μM ATX in the pipette solution, before and after application of 10 μM Me5. (B, C) The scaled currents recorded at 0.3 Hz (B) or 1 Hz (C) after effect of Me5 (continuous lines) well superimposed their respective control current (dashed lines). (D) Bar graph showing the reduction of sodium current measured at the peak (open bars) and at the steady state (filled bars) induced by 50 μM mexiletine (n=4) and 10 μM Me5 (n=4), both in the presence of ATX and at a frequency of stimulation of 1 Hz. Me5 reduces peak and steady-state currents to the same extent whereas mexiletine reduces peak current significantly more than steady-state current.
