Figure 3.
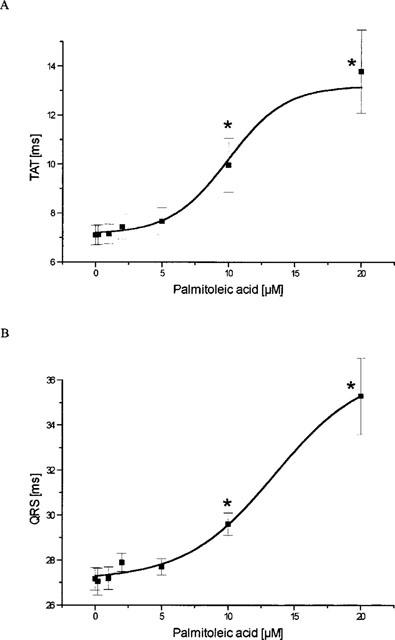
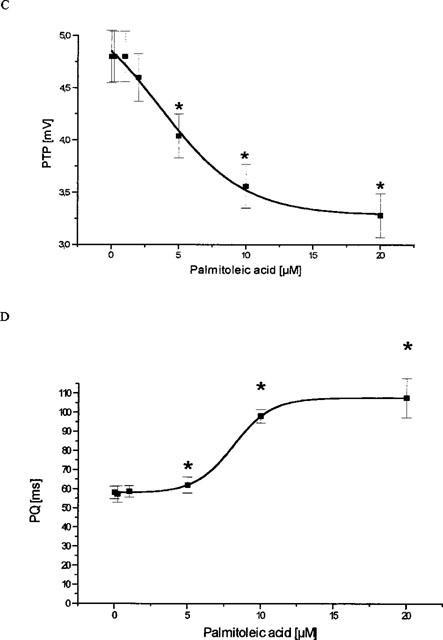
Influence of palmitoleic acid on cardiac ventricular and supraventricular conduction. (A) Effect of palmitoleic acid on ventricular total activation time (TAT), i.e. time necessary to activate the whole ventricular epicardial surface. (B) Action of palmitoleic acid on the width of the ventricular activation signal, i.e. the ventricular QRS complex. (C) Effect on the peak-to-peak-amplitude (PTP) of the ventricular QRS complex. (D) Influence of palmitoleic acid on the atrioventricular conduction time (PQ). In all four panels data are given from n=7 experiments as means±s.e.mean. Significant changes versus control conditions (60 min equilibration) are indicated by an * (P<0.05).
