Figure 2.
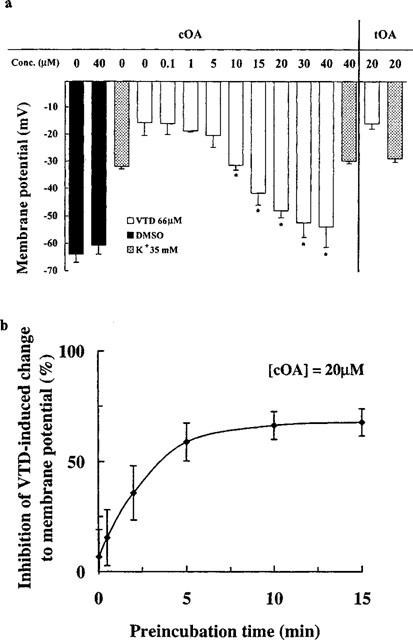
Biochemical data confirming the presynaptic effects of oleamide on mouse nerve terminal polarization and a selective interaction with the voltage-gated Na+ channel. (a) Effect of cOA and tOA on veratridine- (VTD) or K+-induced depolarization of mouse brain synaptoneurosomes. Apparent IC50 for cOA, by probit transformation, was 13.93 μM. Bars depict mean and s.e.mean of 3–4 independent determinations (*P<0.05). (b) Kinetic effects of 20 μM cOA on veratridine-induced (66 μM) depolarization of synaptoneurosomes. Each point represents mean (bars±s.e.mean) of three independent experiments. The data above were determined at equilibrium (15 min preincubation).
