Figure 5.
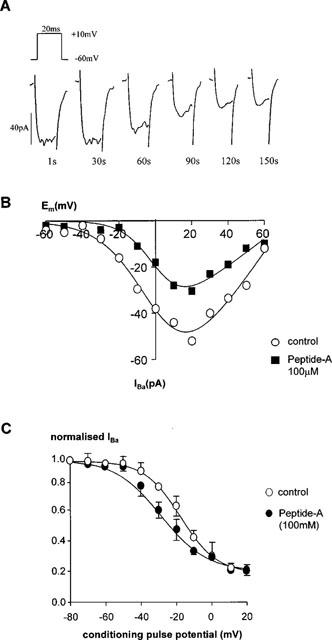
Effect of peptide A on calcium channel currents. (A) Effect of 100 μM peptide-A on a single rabbit ear artery cell. Currents were evoked every 1 s using a 20 ms pulse to +10 mV from a holding potential of −60 mV (upper inset). Peptide-A (100 μM) was applied by inclusion in the intracellular pipette solution. Current traces recorded at 1, 30, 60, 90, 120 and 150 s are shown. (B) The effect of peptide-A on the I-V relationship of calcium channel currents. I-V relationships were derived as described in the legend for Figure 1. The figure shows a representative control cell and a cell dialysed with peptide-A. I-V data were measured when the size of the currents had stabilized. Control and peptide-A-dialysed cells were derived from the same batch of cells. Data are representative of 3–4 similar observations. (C) Steady-state inactivation of calcium channels. Steady-state inactivation curves were derived by using a double pulse protocol as described in the legend for Figure 1. Data are means±s.e.means of three separate experiments.
