Figure 2.
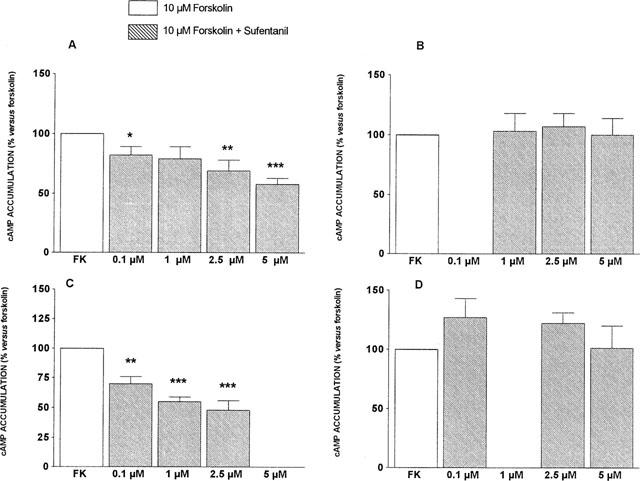
Effects of sufentanil on forskolin induced cyclic AMP accumulation in the different experimental groups. Cyclic AMP was determined in brain cortex slices incubated for 10 min in the presence of 10 μM forskolin alone or with increasing concentrations of sufentanil (0.1–5 μM). (A) Control animals (n=24) were treated with saline (1 μl h−1) for 7 days. (B) Tolerant animals (n=19) received sufentanil (2 μg h−1) for 7 days. (C) Supersensitive animals (n=8) were concurrently treated with sufentanil (2 μg h−1) and nimodipine (1 μg h−1) for 7 days. (D) In the nimodipine withdrawal group (n=5), nimodipine minipump was removed on the 6th day of infusion, while sufentanil minipump remained in place for 7 days. Data are expressed as mean±s.e.mean. Within-group comparisons were performed by one-way ANOVA (Group A: F=7.43, P<0.001; Group B: F=0.15, NS; Group C: F=17.11, P<0.001; Group D: F=1.18, NS). ***P<0.001, **P<0.01,*P<0.05 vs forskolin (Bonferroni test). Four-factor ANOVA was used for comparing sufentanil effects between groups (F=3.31, P=0.001). Bonferroni Post hoc test showed significant differences between control group and tolerant (P<0.001), supersensitive (P<0.01), and nimodipine withdrawal (P<0.001) groups; between supersensitive group and tolerant (P<0.001) and nimodipine withdrawal (P<0.001) groups, but not between tolerant and nimodipine withdrawal groups.
