Figure 5.
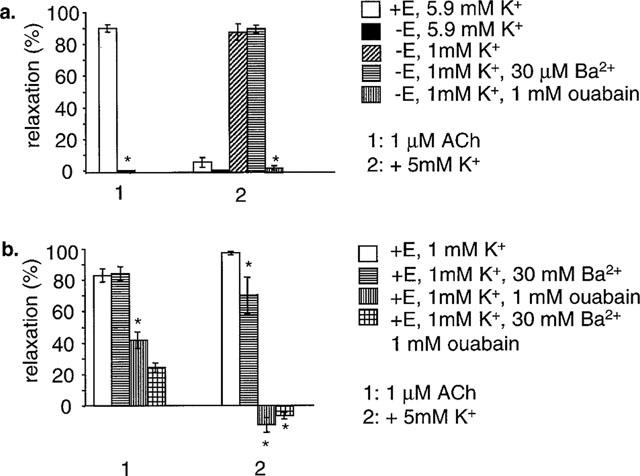
The effects of ouabain and barium in 1.18 mM K+ in isometric arteries. In isometric arteries (wire myography), relaxation to ACh was dependent on the presence of an intact endothelium. K+ failed to induce relaxation (5.9–10.9 mM step) both in the presence and absence of endothelium. (a) Relaxation to K+ was induced in endothelial denuded arteries by lowering [K+] to 1 mM K+, and stepping back to 6 mM. This relaxation was unaffected by 30 μM Ba2+ and abolished by 1 mM ouabain. Mean data for eight arteries are shown. Numbers next to columns are P values compared to the relevant control dilatation in the absence of barium and ouabain. (b) A similar experiment in endothelium-intact arteries. ACh still relaxed in 1 mM K+. This was unaffected by 30 μM Ba2+, and significantly depressed by both 1 mM ouabain, and a combination of 1 mM ouabain and 30 μM Ba2+. K+-induced relaxation was significantly depressed by 30 μM Ba2+, and abolished by 1 mM ouabain and a combination of 1 mM ouabain and 30 μM Ba2+. Mean data for eight arteries are shown. *Shows significance (P<0.05) compared to control.
