Figure 2.
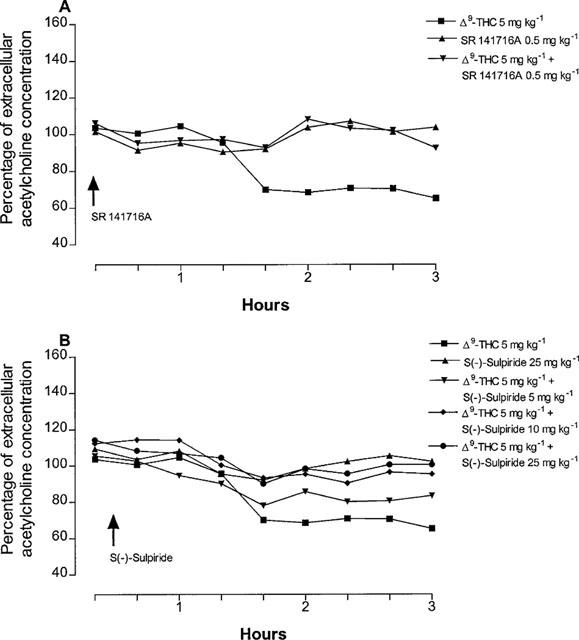
Time-course for the antagonism by SR141716A (A) and S(−)-sulpiride (B) of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced reduction of hippocampal extracellular acetylcholine concentration. (ANOVA main effect Δ9-THC+SR 141716A F1.16=5.35, P<0.05; ANOVA main effect Δ9-THC+S(−)-sulpiride 5 mg kg−1 F1.16=0.42, P=0.52; ANOVA main effect Δ9-THC+S(−)-sulpiride 10 mg kg−1 F1.16=5.83, P<0.05; ANOVA main effect Δ9-THC+S(−)-sulpiride 25 mg kg−1 F1.16=6.97, P<0.05). P<0.05 vs Δ9-THC 5 mg kg−1 (Student-Newman-Keuls test). Data are expressed as percentage (mean±s.e.mean; n=5) of the baseline concentration. Basal values of extracellular acetylcholine concentration, prior to drug administration, were: 1.22±0.11, 1.32±0.18 and 1.41±0.23 for Δ9-THC, SR 141716A and S(−)-sulpiride groups, respectively and 1.25±0.21, 1.23±0.23, 1.45±0.22 fmol μl−1 for the different groups treated with Δ9-THC+S(−)-sulpiride at the doses of 5, 10 and 5 mg kg−1, respectively. SR141716A and S(−)-sulpiride were given 20 and 30 min after Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, respectively. SR141716A and S(−)-sulpiride given alone had no effect on acetylcholine release. s.e. values were not more than ±19.32%.
