Figure 2.
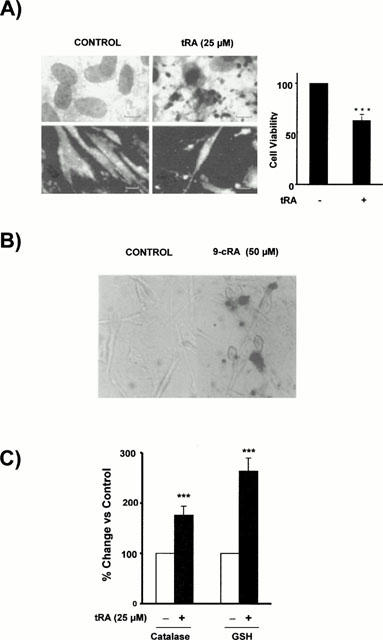
Retinoid-induced apoptosis in CHMC. (A) Effect of high concentrations of tRA on the morphology and viability of CHMC. The left panel shows light microphotographs (upper panels) where apoptotic mesangial cells exhibits nuclear fragmentation into spherical structures and condensed cytoplasm, but they are still surrounded by a cell membrane, and fluorescent microphotographs (lower panels) where several nuclei with condensed chromatin are observed. The right panel shows the decrease in viable cells (as assessed by direct count under light microscopy of cells excluding trypan blue dye) after 24 h incubation with 25 μM tRA (Student's t-test ***P<0.001 vs control). (B) Effect of 9-cRA on DNA fragmentation in cultured human mesangial cells. Cells were incubated for 48 h in control conditions or with 50 μM 9-cRA. Then TUNEL staining was performed using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, an enzyme which catalyzes incorporation of fluorescein-dUTP at sites of DNA breaks. The reaction was amplified by alkaline phosphatase enzyme. Apoptotic cells appear as red nuclei whereas non-apoptotic cells were non-stained. Micrographs correspond to control cells (left) or to 9-cRA incubated cells (right). (C) Effect 25 μM tRA on the catalase activity and reduced glutathione (GSH) content in CHMC. Cells were incubated for 48 h in control conditions or with 25 μM tRA. Then catalase activity and GSH content were measured as described in Methods. (Student's t-test ***P<0.001 vs control).
