Figure 5.
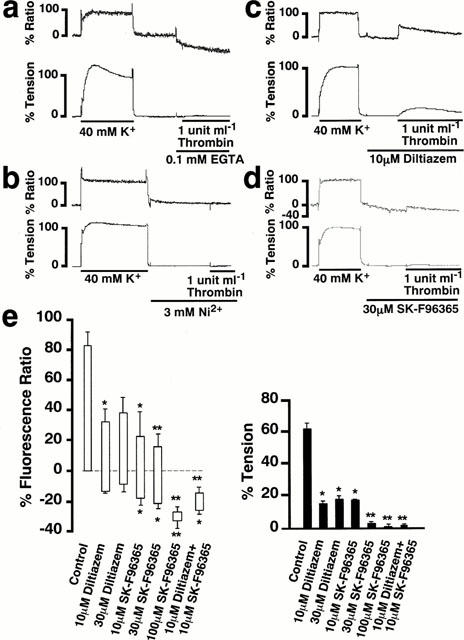
Mobilization of Ca2+ in the pregnant rat myometrium during the thrombin-induced contraction. (a) (b) (c) and (d) Representative traces of the thrombin-induced changes in [Ca2+]i (upper trace) and tension (lower trace) in the pregnant rat myometrium observed in the Ca2+-free PSS containing 0.1 mM EGTA (a), and in the normal PSS containing 3 mM Ni2+ (b), 10 μM diltiazem (c), and 30 μM SK-F96365 (d) in the normal PSS. (e) Summary of the inhibitory effects of diltiazem and SK-F96365 on the thrombin-induced increase in [Ca2+]i and tension. Control; the 1 u ml−1 thrombin-induced [Ca2+]i elevation and tension development in the normal PSS with no inhibitors. The bottom and top levels of columns for [Ca2+]i indicate the values obtained just before the initiation of contraction by thrombin and at the peak contractile response, respectively. The developed tension was evaluated by the area under the tension trace. The [Ca2+]i and developed tension were expressed as a percentage, assigning the values obtained with 40 mM K+ PSS to be 100%. The data are the mean±s.e.mean (n=5–8). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 as compared with the control.
