Figure 6.
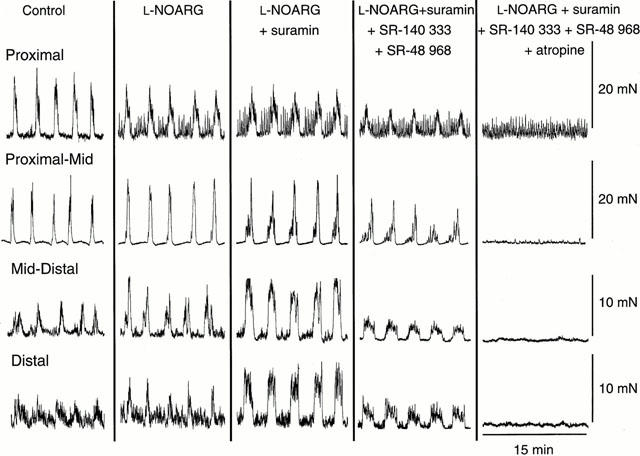
Typical recordings demonstrating the effects of L-NOARG, suramin, SR-140 333 and SR-48 968 and atropine, added sequentially to the organ bath, on MMCs in the proximal, proximal-mid, mid-distal and distal regions of the colon. L-NOARG (100 μM) caused a significant increase in amplitude and integral of MMCs in the distal region, whilst decreasing amplitude and integral in the proximal region. The subsequent addition of suramin (100 μM) caused a further increase in amplitude and integral of MMCs in the distal region, whilst increasing amplitude and integral in the mid-distal region. Both the rapid and long duration contractions of the MMCs were formed after the addition of L-NOARG and suramin. Subsequent addition of SR-140 333 (250 nM) and SR-48 968 (250 nM) significantly reduced MMC amplitude and integral in all regions of the colon whilst preferentially abolishing the long duration component of MMCs. Residual MMCs were abolished by the addition of atropine (1 μM). L-NOARG, suramin and SR-140 333 and SR-48 968 had no effect on MMC frequency in any of the regions. Recordings were made from the same preparation. Scale bars for each region apply throughout. Addition of each drug occurred at least 15 min before the start of the recording shown.
