Figure 2.
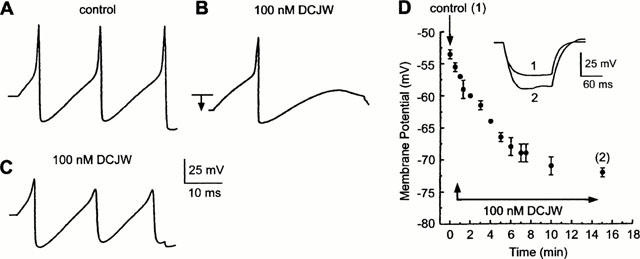
Using the whole cell current-clamp recording configuration, the effect of DCJW on membrane potential and triggered action potentials recorded from an isolated DUM neurone cell body are demonstrated. Action potentials elicited by a 40-ms depolarizing current pulse (0.8 nA) were recorded from an isolated cell body held at −52 mV prior to (A, control) and following the application of 100 nM DCJW (B,C). DCJW reduced the action potential amplitude and produced a large hyperpolarization (B, arrow). Artificial depolarization of the neurone to bring its resting potential back to the control value was ineffective in reversing the DCJW blocking effect (C). (D) The amplitude of the DCJW-induced hyperpolarization is plotted as a function of time of application (n=5). Inset: shows the membrane potential recorded in response to a hyperpolarizing current pulse (150 ms in duration) in saline (control 1) and 15 min (2) after the application of 100 nM DCJW.
