Figure 3.
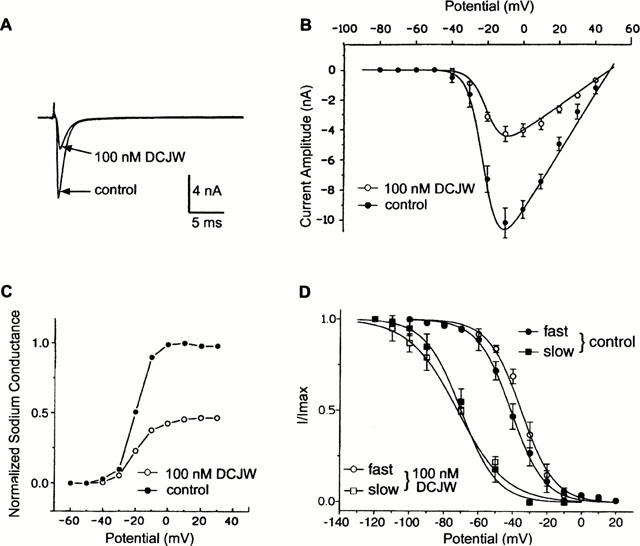
Effects of DCJW on the DUM neurone voltage-dependent inward sodium current. (A) Sodium inward current traces obtained by a 30-ms depolarizing pulse to −10 mV from a holding potential of −90 mV, in the absence (control) and presence of 100 nM DCJW. Currents are leak- and capacity-corrected. (B) Effect of DCJW on the current-voltage relationship of the inward sodium current. The maximum peak current amplitude was plotted versus membrane potential before (control) and after application of 100 nM DCJW. (C) Voltage dependence of the normalized sodium conductance of the inward current was calculated according to equation 2, in normal saline (control) and after the application of 100 nM DCJW. (D) Superimposed voltage dependence of the fast and slow steady-state inactivation curves of the inward sodium current in normal saline (control) and in the presence of 100 nM DCJW. The smooth lines are fitted through the mean data points using the single Boltzmann distribution (equation 3). Data are means±s.e.mean.
