Figure 1.
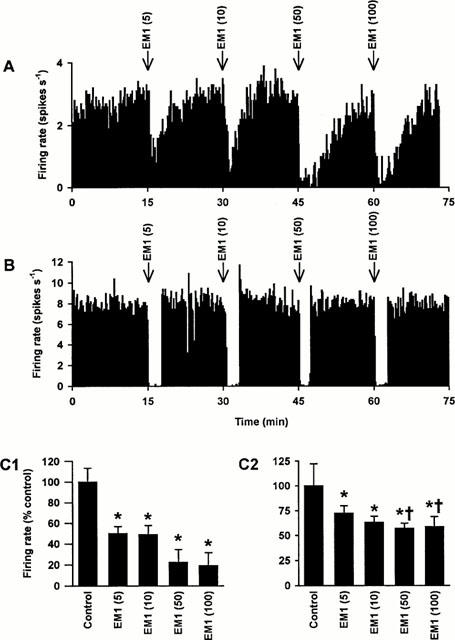
Effects of i.c.v. endomorphin 1 on the activity of oxytocin and vasopressin cells in urethane-anaesthetized rats. (A) The firing rate (averaged in 10 s bins) of a SON oxytocin cell (excited after 20 μg kg−1 CCK i.v.; not shown) recorded from a urethane-anaesthetized rat. This cell was inhibited by endomorphin 1 (5, 10, 50 and 100 pmol, i.c.v.; EM1). (B) The firing rate (averaged in 10 s bins) of a SON vasopressin cell recorded from a urethane-anaesthetized rat. Again, this cell was inhibited by endomorphin 1 (5, 10, 50 and 100 pmol, i.c.v.). (C) The panels show the firing rate (+s.e.mean, averaged over 5 min) of SON oxytocin (C1; n=9) and vasopressin (C2; n=7) cells recorded from rats injected with endomorphin 1 (5, 10, 50 and 100 pmol, i.c.v.). Two-way RM ANOVA revealed significant effects of endomorphin 1 (P<0.0001), significant differences between the responses of oxytocin and vasopressin cells (P=0.005) and a significant interaction between the dose of endomorphin 1 and cell type (P=0.01). *P<0.05 versus control and †P<0.05 versus the equivalent endomorphin 1 dose in oxytocin cells; Student-Newman-Keuls post-hoc tests.
