Figure 1.
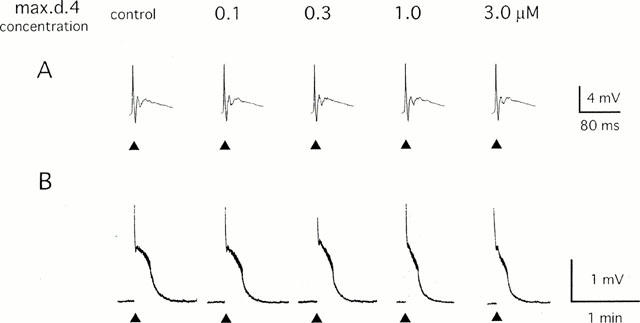
Effect of max.d.4 on the primary afferent evoked potential in the neonatal rat spinal cord. A single-shock stimulus (200 μs 20 V) was given to the dorsal root (L4) at the time indicated by ▴ and the potential was recorded extracellularly from the ispilateral ventral root. Max.d.4 was applied to the spinal cord in a cumulative manner. (A) Sample records of the fast time course monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes that were stored in a transient memory device and recorded by a pen recorder with a 500 fold expansion of the time base. (B) Sample records of slow ventral root potential (VRP) recorded by a pen recorder.
