Figure 1.
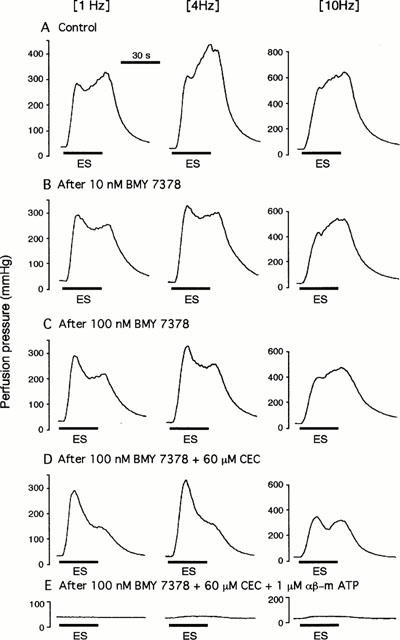
Double peaked vasoconstrictor responses to periarterial electrical nerve stimulation and the effects of BMY 7378, CEC and αβ-m ATP in an isolated, perfused canine splenic artery. The double peaked vasoconstrictions were induced by 30 s trains of pulses at 10 V amplitude and 1 ms pulse duration, with a frequency of 1, 4 or 10 Hz (A). At low frequences (1 and 4 Hz), pretreatment with BMY 7378 (10 – 100 nM) produce a dose-dependent inhibition on the second peaked responses without inhibition of the first peaked response. At a high frequency of 10 Hz, both the first and second peaks were reduced by BMY 7378 (B,C). A subsequent administration of CEC (60 μM) additionally inhibited those responses in the presence of 100 nM BMY 7378 (D). The remaining responses after treatment with BMY 7378 and CEC were abolished by 1 μM αβ-m ATP (E). (ES), Periarterial electrical nerve stimulation.
