Figure 5.
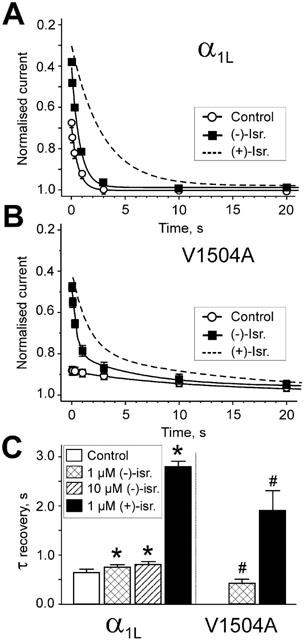
Recovery of α1L/α2-δ/β1a and V1504A channels from (+)- and (−)-isradipine-induced inactivation. Time course of IBa recovery from (−)-isradipine-induced inactivation after a 3 s conditioning prepulses to 20 mV (holding potential −80 mV). Test pulses to 20 mV were applied at various time intervals after the conditioning pulses. Peak IBa during the test pulses were normalized to peak IBa measured during the conditioning prepulse. Smooth curves in panels represent mono- or biexponential functions fitted to IBa recovery of α1L/α2-δ/β1a (A) and V1504A (B) channels in control and in 1 μM (−)-isradipine. The parameters of fit were in (A) for control recovery (○): A=0.33, τ=0.61 s, C=1; recovery in 1 μM (−)-isradipine: A=0.63, τ=0.74 s, C=0.97. Broken line illustrates the corresponding time course of IBa recovery in 1 μM (+)-isradipine (fitted curve form Berjukow et al., 2000). (B) Recovery of V1504A in control (○): Aslow=0.11, τslow=13.4 s, C=0.98 and the presence of 1 μM (−)-isradipine: Afast=0.42, τfast=0.39 s, Aslow=0.21, τslow=11.1 s, C=0.98. Dashed line illustrates recovery of IBa in 1 μM (+)-isradipine (data from Berjukow et al., 2000). (C) Time constant of recovery from fast inactivation in control (white column), 1 μM and 10 μM (−)-isradipine (hatched columns). Black columns illustrate the corresponding recovery from (+)-isradipine-induced inactivation (data from Berjukow et al., 2000). α1L/α2-δ/β1a and V1504A channels recover significantly faster from (−)-isradipine-induced inactivation compared to (+)-isradipine. Note that the inactivation deficient mutant V1504A recovered faster from (+)- and (−)-isradipine-induced inactivation than α1L/α2-δ/β1a channels (*P<0.01 compared to α1L/α2-δ/β1a in control. #P<0.01 compared to recovery of the respective enantiomers in α1L/α2-δ/β1a).
