Figure 1.
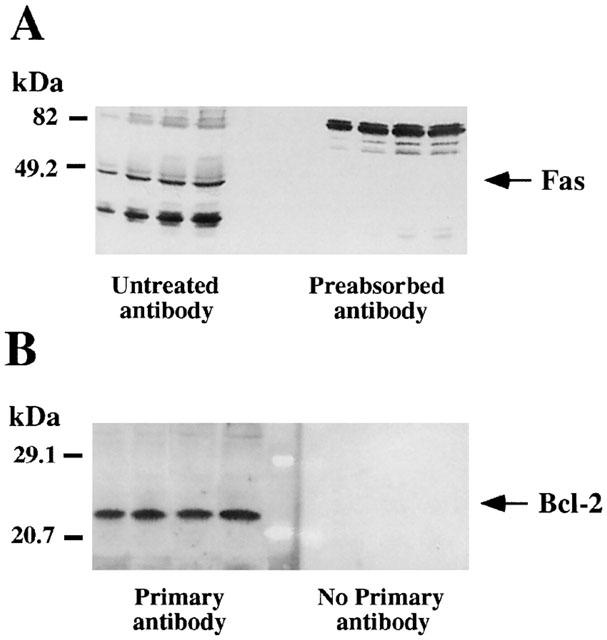
Representative autoradiographs of Western blots depicting labelling of immunodetectable pro-apoptotic Fas receptor (A) and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 oncoprotein (B) in rat brain membranes. Samples from the cerebral cortex were subjected to SDS – PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (immunoblotting), incubated with the specific primary and secondary antibodies, and visualized by the Enhanced Chemiluminiscence (ECL or ECL-Plus) method. The apparent molecular masses of Fas (48/49 kDa) and Bcl-2 (25/26 kDa) proteins were determined by calibrating the blots with prestained molecular weight markers as shown on the left hand side. For Fas the amounts of total protein loaded per gel well were: 31.4; 62.7; 94.1; 125.4 (μg) and the corresponding IOD: 0.37; 0.75; 1.08; 1.21 (arbitrary units) (standard curve; μg protein vs IOD, r=0.98). For Bcl-2 the amounts of total protein loaded per gel well were: 31.4; 62.7; 94.1; 125.4 (μg) and the corresponding IOD: 0.56; 1.29; 2.48; 2.90 (arbitrary units) (standard curve; μg protein vs IOD, r=0.99). (A) The specificity of the antibody anti-Fas was assessed by preincubating the antibody with the antigenic peptide (preabsorbed antibody), which resulted in the blockade of the immunoreaction for the specific protein (48/49 kDa) and other unknown related peptides (≈35 – 40 kDa). (B) For Bcl-2 immunodetection, omission of the primary antibody was used as a negative control and the immunoreactivity was absent under this condition.
