Figure 4.
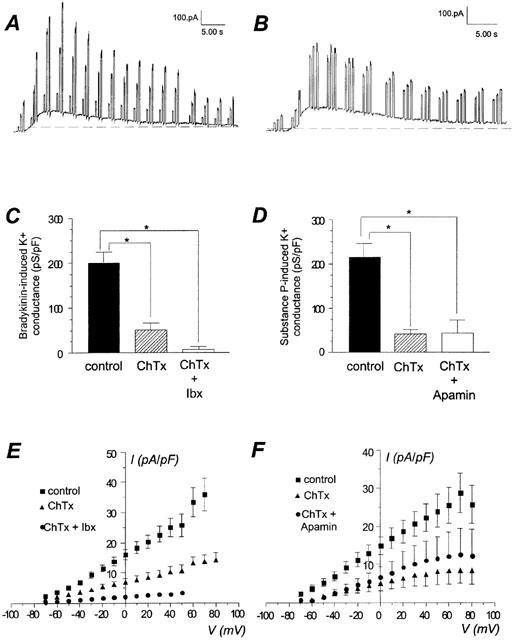
Effect of peptide toxins on maximal conductance stimulated by bradykinin and substance P in whole-cell configuration. (A, B) Original recordings of a response to bradykinin and substance P, respectively. Holding potential was −50 mV, voltage steps (−20, 20, 40 mV) were repetitively applied. (C) Comparison of the whole-cell bradykinin-induced maximal K+ conductance in control condition (100 nM), in the presence of charybdotoxin alone (50 nM, ChTx), or a mixture of charybdotoxin and iberiotoxin (50 nM each inhibitor, ChTx+Ibx). E, current-voltage relationship of the bradykinin-stimulated current in control condition, in presence of charybdotoxin alone (ChTx), or a mixture of charybdotoxin and iberiotoxin (ChTx+Ibx). Data are the mean±s.e.mean of 4–24 experiments. (D) Comparison of the whole-cell substance P-induced maximal K+ conductance in control condition (100 nM), in the presence of charybdotoxin alone (50 nM, ChTx), or a mixture of charybdotoxin (50 nM) and apamin (1 μM, ChTx+Apamin). (F) Current-voltage relationship of the substance P-stimulated current in control condition, in presence of charybdotoxin (ChTx) alone, or a mixture of charybdotoxin and apamin (ChTx+Apamin). Data are the mean±s.e.mean of 8–17 experiments. *For P<0.05 vs control condition.
