Figure 3.
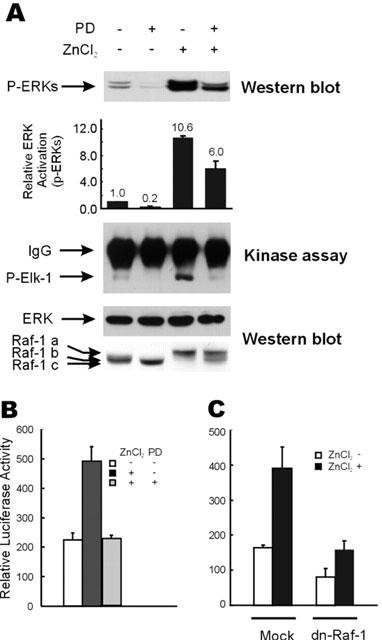
Down-regulation of the zinc-induced activation of the ERK pathway by inhibition of MEK or Raf-1 kinases. (A) HT29 cells were serum starved as described in Figure 1A, and treated with 100 μM of ZnCl2 for 9 h before harvesting for extract preparation. In required cases, cells were incubated with 10 μM of PD98059 for 30 min before zinc treatment. Western blot analysis was performed to visualize the phospho-ERK, Raf-1, and ERK protein bands. Phospho-ERK levels were quantitated by densitometric scanning of phospho-ERK protein bands. Relative ERK activations are average values of the results of three independent Western blot analyses. The in vitro kinase activity of ERKs was measured using purified GST-Elk-1 substrate, as described by the manufacturer (New England Biolab Inc.). (B) HT29 cells were grown and transfected with pFR-Luc and pFA2-Elk-1 vectors as in Figure 2B, except that 10 μM of PD98059 was administered 30 min prior to treatment with 100 μM ZnCl2, in the required cases. Elk-1 dependent trans-reporter gene expression was measured 12 h after treatment with 100 μM of ZnCl2. (C) After transfection with 0.5 μg of pFR-Luc and 25 ng of pFA2-Elk-1 plasmids, HT29 cells were serum starved and treated with 100 μM ZnCl2. In selected cases, 0.5 μg of the pSV-Sport1 vector or pSV-Sport1-Raf-1-dn was cotransfected together with the plasmids mentioned above. Elk-1 dependent trans-reporter gene expression was measured 12 h after treatment with 100 μM of ZnCl2.
