Figure 7.
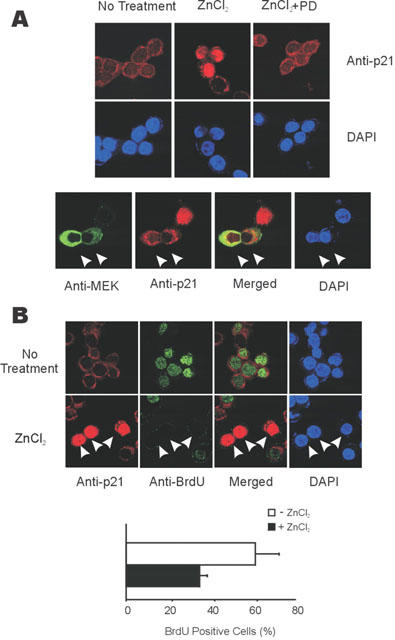
ERK pathway dependent nuclear localization of p21Cip/WAF1 inhibits BrdU incorporation. (A) Nuclear localization of p21Cip/WAF1 induced by zinc and inhibited by PD98059 (upper panel) or by the expression of MEK-2A (lower panel). Upper panel; HT29 cells were treated or not treated with 100 μM of ZnCl2 for 9 h before immunocytochemistry. In the required cases, they were incubated PD98059 (10 μM) for 30 min before treatment with zinc. Lower panel; HT29 cells were grown and transfected with 0.5 μg of pCMV-MEK-2A. The cells were treated with 100 μM of ZnCl2 for 9 h before immunocytochemistry. The expression and localization of p21Cip/WAF1 and MEK-2A was revealed by immunocytochemistry using the anti- p21Cip/WAF1 antibody together with Rhodamin-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG, or anti-MEK antibody together with Cy-2-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody; nuclei were stained by DAPI. The representative cells inhibiting induction and nuclear localization of p21Cip/WAF1 by expressing MEK-2A were marked by arrows. (B) Inhibition of BrdU incorporation by induction and nuclear localization of p21Cip/WAF1 by zinc. Upper panel; Zinc dependent induction and nuclear localization of p21Cip/WAF1 inhibited BrdU incorporation. HT29 cells were serum starved with the media containing 1% FBS, then further grown in the media without or with 100 μM ZnCl2 for 16 h. The cells were labeled with 20 μM of BrdU for last 12 h before assay. BrdU incorporated nuclei were revealed with green colour by immunocytochemistry by using anti-BrdU antibody followed by Cy2-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The representative zinc treated cells blocked the BrdU incorporation by induction and nuclear localization of p21Cip/WAF1 was marked by arrows. Lower panel; The percentage of cells incorporating BrdU was lowered by 100 μM of ZnCl2 treatment. BrdU positive cell data was quantified from the results of upper panel.
