Figure 4.
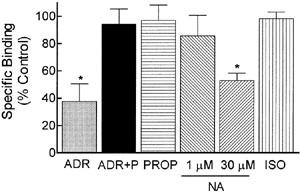
Chronic ADR treatment down-regulates α2-ARs. BE(2)-C cells were incubated for 16–24 h with vehicle (0.1 mM ascorbate), 300 nM ADR, 30 nM propranolol, ADR+30 nM propranolol, 1 μM NA, 30 μM NA or 1 μM ISO. Specific binding to cell membrane homogenates was calculated by subtracting the binding of a single concentration of radioligand (2 nM) in the presence of phentolamine (10 μM) from the binding in its absence. ADR profoundly down-regulated α2-AR levels, but this down-regulation was blocked by the β-AR antagonist, propranolol (*P<0.05 by ANOVA). Chronic 30 μM NA treatment also reduced α2-AR levels while ISO, 1 μM NA or propranolol alone had no effect. Data are presented as mean±s.e.mean of 3–5 independent experiments; α2-AR binding in control cells was 1143±283 c.p.m. mg−1 protein.
