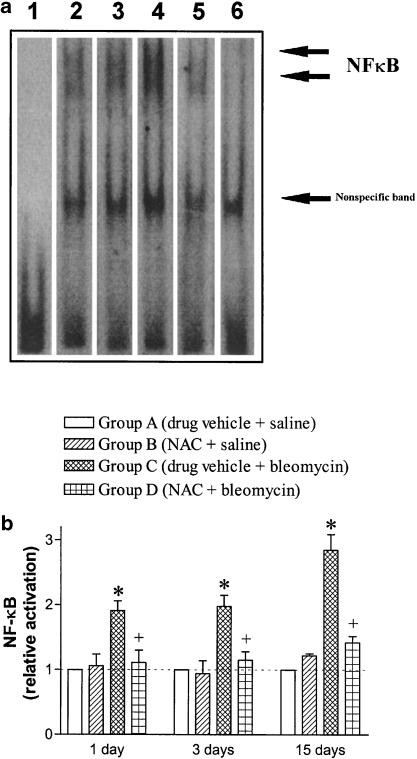
Figure 4.
Effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC; 300 mg kg−1 per day, i.p.) on the bleomycin-induced increase of NF-κB-binding activity assessed at 1, 3 and 15 days postexposure. Panel (a) An electrophoretic gel mobility shift assay showing NF-κB-binding activity in rat lung cell nuclear proteins from individual animals at 1 day postbleomycin. Lane 1: Free probe. Lanes 2, 3, 4 and 5 correspond to experimental groups A (drug vehicle + saline), B (NAC + saline), C (drug vehicle + bleomycin) and D (NAC + bleomycin), respectively. The specificity of the binding was confirmed by adding excess unlabelled NF-κB oligonucleotide (lane 6). Panel (b) The densitometric scanning of the band shift data of NF-κB-binding activity is expressed as relative values compared to their corresponding values in group A taken as unity. There was a significant increase in NF-κB-binding activity that was suppressed in NAC-treated rats. Columns are means±s.e.m. of three to four independent experiments for each group. *P<0.05 compared to group A; +P<0.05 from group B.