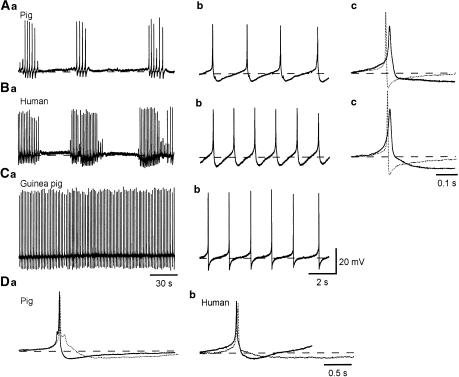
Figure 1.
Comparison of action potentials in the human, pig and guinea-pig bladder. Detrusor smooth muscle cells of the pig and human bladder exhibited bursts of action potentials (Aa, Ba), which had an amplitude of some 40 mV and consisted of a slow depolarizing phase and a regenerative depolarization which lasted for some 20 ms (Ab, Bb). The regenerative depolarization of the inter-burst action potentials was followed by a repolarizing phase which continued to a fast AHP (Ab, Bb). Overlaid traces show action potentials recorded from pig or human (full lines) and guinea-pig (dotted line) bladders (Ac, Bc). Note that the AHP of the guinea-pig bladder is sharper and of shorter duration than the fast AHP in the other species. Continuous action potentials recorded from the guinea-pig bladder (Ca) had an amplitude of some 50 mV, and consisted of a slow depolarizing phase and a rapid regenerative depolarizations which lasted less than 10 ms. The depolarizations were followed by a rapid repolarizing phase and an AHP (Cb). The types of AHP in pig and human bladder are shown in Da and Db. Full lines show action potentials followed by a fast AHP characteristic of the inter-burst action potentials and dotted lines show action potentials followed by a slow AHP, characteristic of preparations showing sporadic or complex action potentials. Resting membrane potentials were −43 mV for A, −41 mV for B and −42 mV for C.