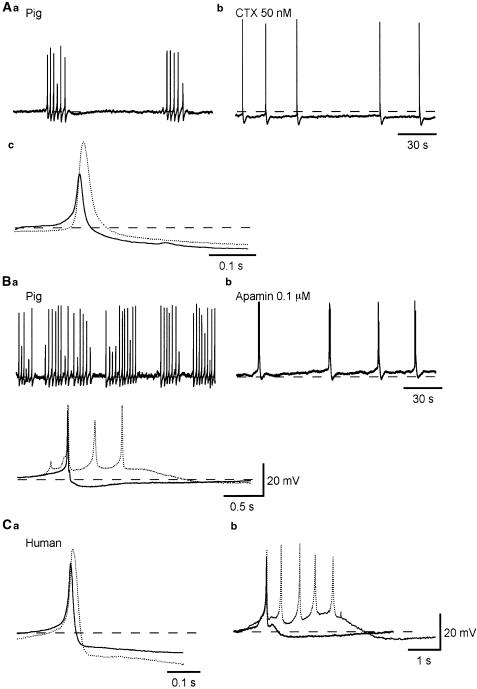
Figure 4.
Effects of CTX and apamin on spontaneous action potentials recorded from pig and human bladder smooth muscles. Bladder smooth muscle cells of the pig exhibiting bursts of action potentials (A, B) in control conditions, had action potentials with an amplitude of about 35 mV, which were followed by a fast AHP (Aa,c). After some 10 min exposure to CTX (50 nM), the membrane was hyperpolarized by some 5 mV and action potentials occurred individually with a reduced frequency (Ab). In the presence of CTX, action potentials had an amplitude of some 60 mV and were followed by a fast AHP (dotted line, Ac). In another preparation exhibiting bursts of action potentials (B), action potentials had an amplitude of about 40 mV, and were followed by a fast AHP in control conditions (Bb,c). After some 10 min exposure to apamin (0.1 μM), the membrane was depolarized by a few mV and complex action potentials were generated (Bb,c). In the presence of apamin, each action potential complex consisted of three to six action potentials and was followed by a slow AHP (dotted line, Bc). In a preparation of human detrusor, similar effects of CTX (dotted line, Ca) and of apamin (dotted line, Cb) were seen. In (Ca) and (Cb), full lines represent control action potentials. Resting membrane potentials were −39 mV in (A), and −43 mV in (B) and −41 mV in (C).