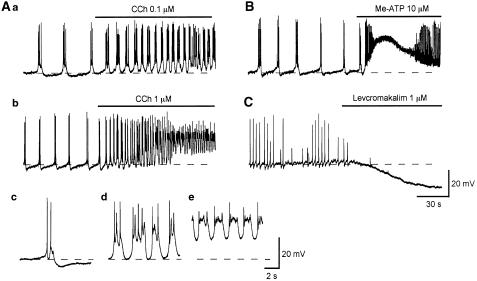
Figure 6.
Effects of CCh, Me-ATP and levcromakalim on spontaneous action potentials recorded from pig-bladder smooth muscle. In a control solution, bladder smooth muscle of pig exhibited spontaneous action potentials (Aa). CCh (0.1 μM) depolarized the membrane by about 3 mV, and increased the action potential frequency (Aa). In another preparation, a higher concentration of CCh (1 μM) depolarized the membrane by some 20 mV and greatly increased action potential frequency (Ab). Me-ATP (10 μM) caused a transient depolarization with an amplitude of some 25 mV which returned to the original level within some 2 min (B). On the rising phase of the depolarization, action potential frequency was dramatically increased and their amplitude was suppressed (B). In a different preparation, levcromakalim (1 μM) hyperpolarized the membrane by about 20 mV and prevented the generation of action potentials (C). Resting membrane potential was −40 mV in (Aa), −41 mV in (Ab and B) and −40 mV in (C).