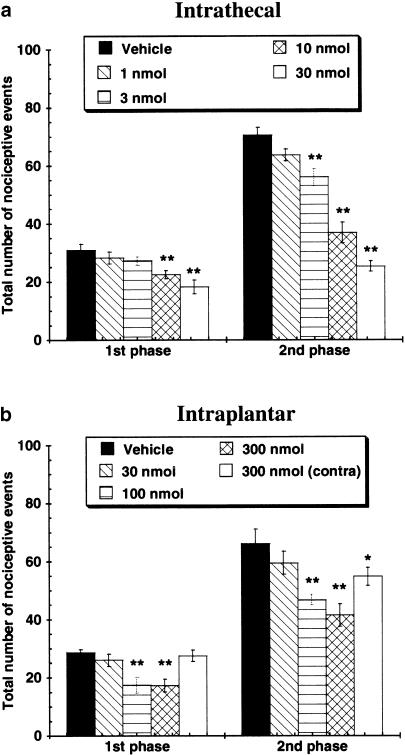
Figure 4.
Effects of (a) intrathecal and (b) intraplantar administration of A-317491 on formalin-induced nocifensive behaviors. Following intradermal injections of formalin (5%) into the dorsal surface of the right hindpaw, the total number of nocifensive events (paw flinching, licking, guarding) was counted during the first (1–15 min) and second (30–50 min) phases of this model. Intrathecal and intraplantar injections of A-317491 were effective, in both phases, to reduce the number of formalin-induced nociceptive behaviors. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs vehicle control group, values are ±s.e.m. (n=5–6 per group).