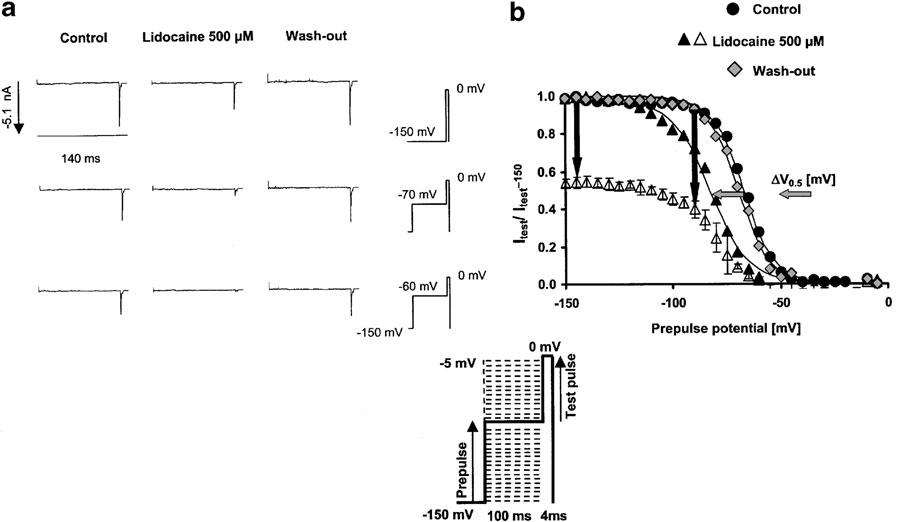
Figure 1.
Effects of lidocaine on fast-inactivated channels, assessed by shifts in the steady-state availability curve. (a) (Left): Representative current traces in the control condition and with 500 μM lidocaine during short (4 ms) test pulses to 0 mV, following a 100 ms prepulse to either −150 mV (first row of traces), −70 mV (second row of traces), or a membrane potential close to the potential for half-maximum channel inactivation in the controls (−60 mV). There is no current activation during the prepulse from −150 mV to the indicated prepulse potential. All current traces elicited by the test pulses have been scaled to maximum value at −150 mV prepulse potential, indicated at the left of the first row. The traces show the increase in peak current suppression achieved by lidocaine at more depolarized prepulse potentials. (b) (Right): Steady-state availability curves assessed by a two-pulse protocol in the absence (control; circles, wash out; rhombs) and presence of 500 μM lidocaine (triangles). Each symbol represents the mean fractional current derived from at least three different experiments, elicited by a 4 ms test pulse to 0 mV, following a 100 ms inactivating prepulse from −150 mV to the indicated prepulse potential. Currents were normalized to maximum value (in each series at −150 mV prepotential); solid lines represent the best Boltzmann fit (equation (2)) to the data with the indicated parameters for control and test, respectively. Error bars are standard deviations. Currents were normalized either to maximum values in the presence of drug (filled symbols) or to maximum values in the controls (empty symbols). Vertical arrows show the increase in the peak current suppression induced by 500 μM lidocaine at more depolarized holding potentials vs hyperpolarized holding potentials. This reduction in channel availability at depolarized prepotentials resulted in a voltage shift in the midpoints of the availability curve (ΔV0.5), indicated by the horizontal arrows.