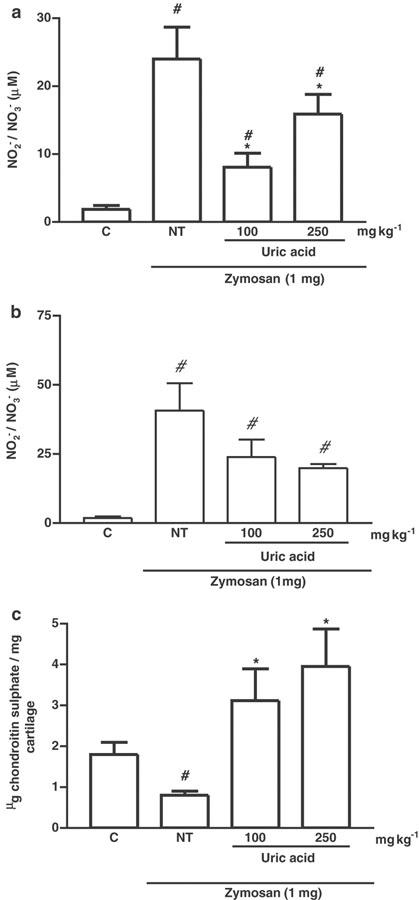
Figure 4.
Effect of UA administration on articular and systemic NO production and articular joint damage 14 days after induction of zymosan arthritis. The production of NO, as determined by measurement of NO2− and NO3−, is shown in (a) joint exudates and (b) peripheral blood. The joint damage was determined by measurement of the GAG content, in articular cartilage samples of rats, as shown in (c). Zymosan was injected i.art. into both knee joints and the NO release in exudates (as NO2− and NO3−) or peripheral blood was measured at 14 days after zymosan. UA (100 or 250 mg kg−1 i.p.) was injected 30 min before zymosan and four times daily, until sacrifice, at 14 days. NT rats received zymosan i.art., but were given (i.p.) saline in order to act as vehicle control. Control (C) animals received only saline i.art. and no systemic treatment. Results are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. of values for each group of six animals. #P<0.05 compared to C rats; *P<0.05 compared to NT rats.