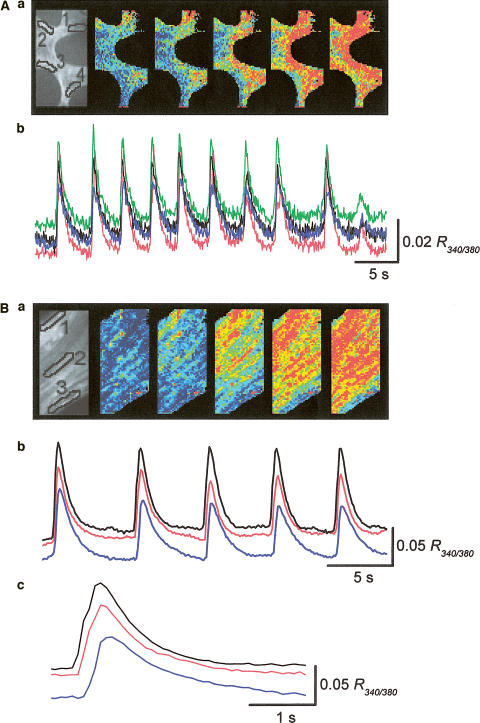
Figure 2.
Calcium waves in the corporal smooth muscle meshwork. (A) Changes in [Ca2+]i were simultaneously recorded from separate areas located with a separation between each area of some 100 μm. The series of frames show Ca waves originating from two separate sites and spreading throughout the tissue within the imaged area (Aa). When changes of [Ca2+]i were simultaneously recorded from four different areas, transient increase in [Ca2+]i occurred synchronously in all areas (Ab). (B) Changes in [Ca2+]i were simultaneously recorded from three separate areas located on the muscle bundle, with a separation between each area of some 40 μm. The series of frames demonstrate a Ca wave originating from the boundary of the muscle bundle and spreading to the other boundary (Ba). When changes of [Ca2+]i were simultaneously recorded from each area, synchronous increase in [Ca2+]i occurred in all areas (Bb). Ca2+ transients recorded from the areas had almost identical time courses, but a delay of some 200 ms was observed between the rising phases of Ca transients in both boundaries (Bc). Black, red and blue traces were recorded from areas 1, 2 and 3, respectively.