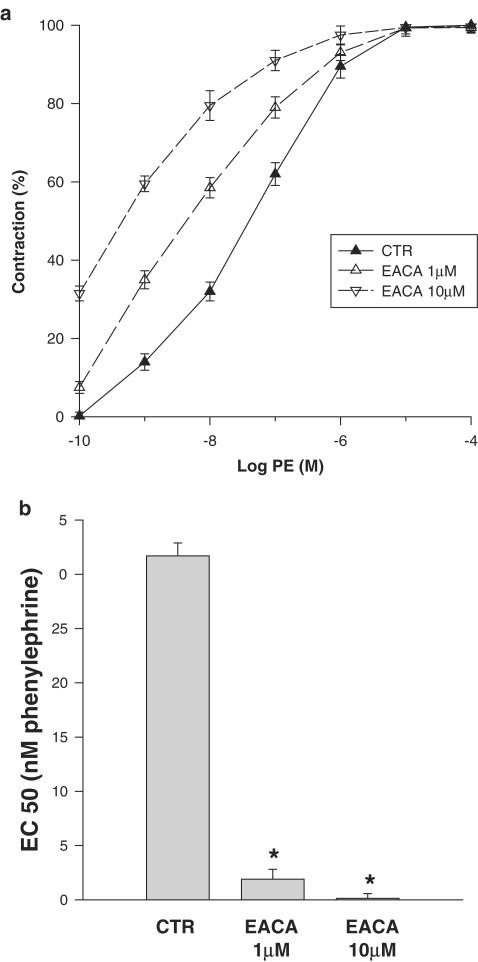
Figure 3.
Effect of EACA on isometric contraction of vascular smooth muscle. (a) Isometric tension was determined in isolated aortic rings incubated with PE. The PE concentration–contraction curve determined in control Krebs–Henselite solution is shifted to the left by the addition of EACA (1 and 10 μM). Each point along these curves represents the mean of 3–9 experiments. (b) Effect of EACA on half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) of PE in isometrically contracted aortic rings: EC50, defined as the PE concentration that induces 50% of the maximal contraction, extrapolated from (a), significantly falls with the addition of EACA (*P<0.001 vs controls for both concentrations of EACA).