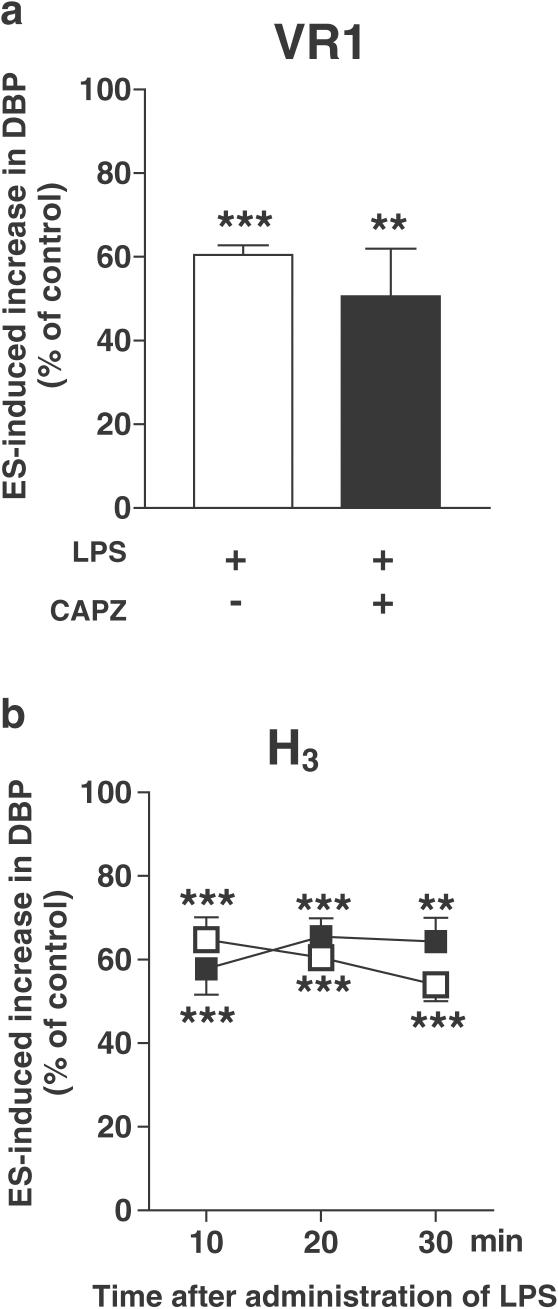
Figure 7.
Influence of the vanilloid VR1 receptor antagonist capsazepine (a) and the histamine H3 receptor antagonist clobenpropit (b) on the inhibition of the electrically induced increase in basal DBP by LPS (4 mg kg−1) in pithed and vagotomized rats. The preganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers were subjected to up to four periods (S1–S4) of ES (1 Hz, 1 ms, 50 V for 10 s). Capsazepine 1 μmol kg−1 (CAPZ, filled bar) was administered 2 min before S1 and 2 min before S3; clobenpropit 0.1 μmol kg−1 (filled squares) was injected 5 min before S1. For further details of the experimental protocol, see Figure 1. Both for animals exposed and not exposed (open bar, open squares) to the antagonists, the ratios S2/S1, S3/S1 and S4/S1 for the increase in DBP obtained in the presence of LPS were expressed as percentages of the corresponding ratios obtained in animals treated with the vehicle for LPS (control). With respect to capsazepine, only the S3/S1 ratio was determined. Means±s.e.m. of 4–8 rats. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared to the corresponding control.