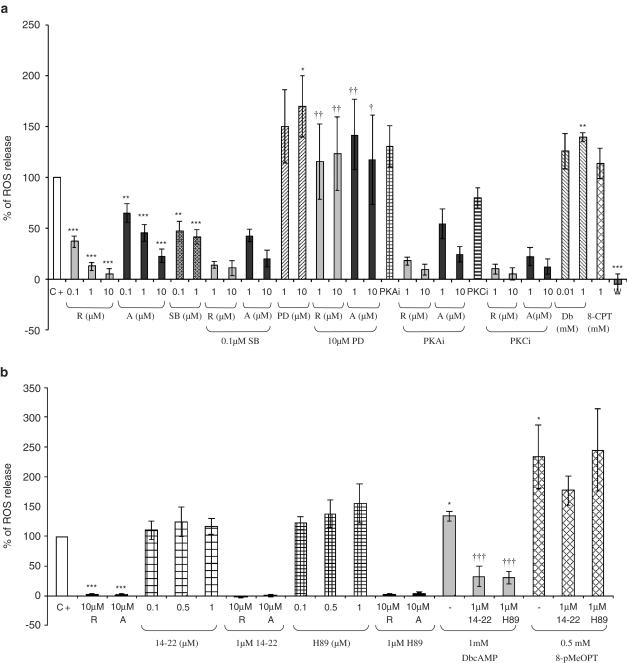
Figure 2.
(a) Percentage of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in bronchoalveolar lavages (containing 90% neutrophils) of LPS-treated rats 10 min after fMLP (2 μM) addition in the presence of MAPK inhibitors, PKA inhibitor or PKC inhibitor and/or PDE4 inhibitors (C+=positive control, R=rolipram, A=Ariflo, SB=SB203580, PD=PD98059, PKAi=0.05 μM protein kinase A inhibitor 14–22 amide myristoylated, PKCi=0.4 μM protein kinase C inhibitor, W=0.05 μM wortmannin). This figure represents the results of 15 experiments. (b) Percentage of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in bronchoalveolar lavages (containing 90% neutrophils) of LPS-treated rats 10 min after fMLP (2 μM) addition in the presence of cAMP analogs (DbcAMP=1 mM, 8-pMeOPT=1 mM 8-pMeOPT-2′-O-Me-cAMP), PKA inhibitors (14–22=0.1–1 μM protein kinase A inhibitor 14–22 amide myristoylated, H-89=0.1–1 μM) and/or PDE4 inhibitors (R=10 μM rolipram, A=10 μM Ariflo). This figure represents the results of five experiments. Statistical analysis for (a) and (b): the effects of each compound were compared to a theoretical mean of 100% representing the positive control (*P<0.01, **P<0.001, ***P<0.0001), and the effects of rolipram or Ariflo in the presence of MAPK, PKA, PKC inhibitors or cAMP analogs were compared to the effects of rolipram or Ariflo alone (†P<0.01, ††P<0.001, †††P<0.0001), using the Holm's multiple test procedure.