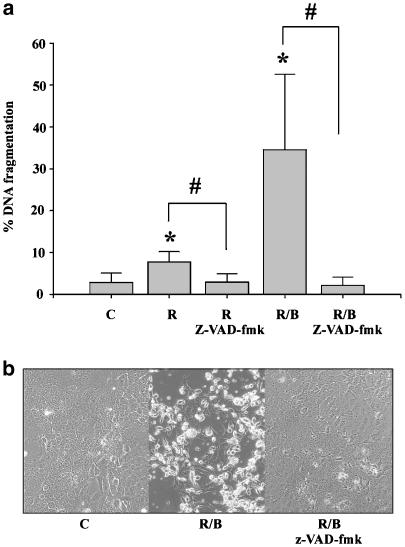
Figure 3.
Induction of apoptosis by ritonavir plus butyrate in DLD-1 cells is potently suppressed by coincubation with z-VAD-fmk. (a) DLD-1 cells were either kept as unstimulated control (C, 0.1% DMSO), or were stimulated with ritonavir (R, 60 μM), with ritonavir plus z-VAD-fmk (30 μM), with ritonavir/butyrate (B, 5 mM), or with with ritonavir/butyrate plus z-VAD-fmk. After 20 h, DNA fragmentation was quantified using the diphenylamine reaction. Data are shown as the mean percentage of DNA fragmentation±s.d. (n=4). *P<0.05 compared to unstimulated control; #P<0.05 compared to ritonavir or ritonavir/butyrate in the absence of z-VAD-fmk. (b) Protective effects of z-VAD-fmk in the same experimental setting as shown by light microscopy.