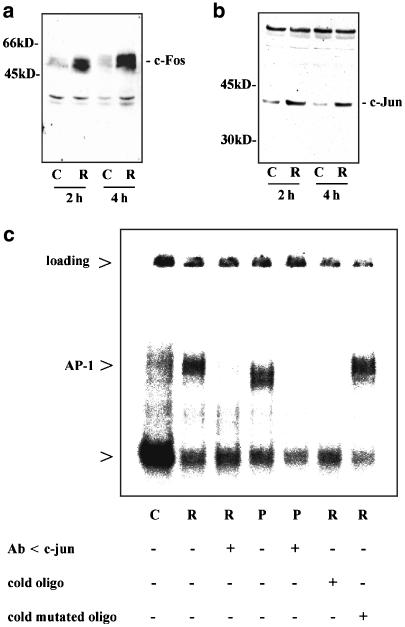
Figure 8.
Ritonavir activates the AP-1 signaling pathway in DLD-1 cells. (a and b) ritonavir induces expression of c-Fos and c-Jun in DLD-1 cells. DLD-1 cells were kept as unstimulated control (C, 0.1% DMSO) or were stimulated with ritonavir (R, 60 μM). After the indicated time periods, cells were harvested and homogenates (140 μg total protein/lane) were assayed for c-Fos (a) or c-Jun (b) protein expression by immunoblot analysis. One representative of three independent experiments performed analyzing ritonavir-induced c-Fos and c-Jun expression is shown. (c) Detection of ritonavir-induced AP-1 DNA binding activity in DLD-1 cells by EMSA analysis. DLD-1 cells were incubated as unstimulated control (C, 0.1% DMSO), or stimulated with ritonavir (R, 60 μM), or with PDTC (PDTC, 200 μM) for 2 h. Thereafter, nuclear extracts were prepared and EMSA analysis was performed using 32P-labeled AP-1 consensus oligonucleotide. As indicated, experiments were performed in the presence or absence of an anti-c-Jun antibody, or of excess cold wild-type or mutated oligonucleotide.